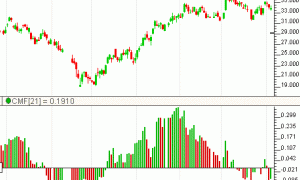
Chaikin Money Flow (CMF)
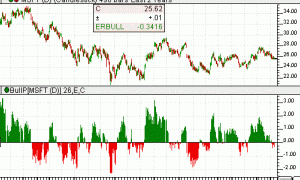
The Chaikin Money Flow indicator (CMF) is calculated by summing Accumulation Distribution over the given period and then dividing by the sum of volume over the given period, as can be seen in the formula section above. A period of 21 is recommended. The volume is essentially nothing more than volume times change divided by range. A positive CMF value signals accumulation, while a negative CMF value signals distribution. A reference line is drawn at zero to help quickly identify accumulation/distribution regions.