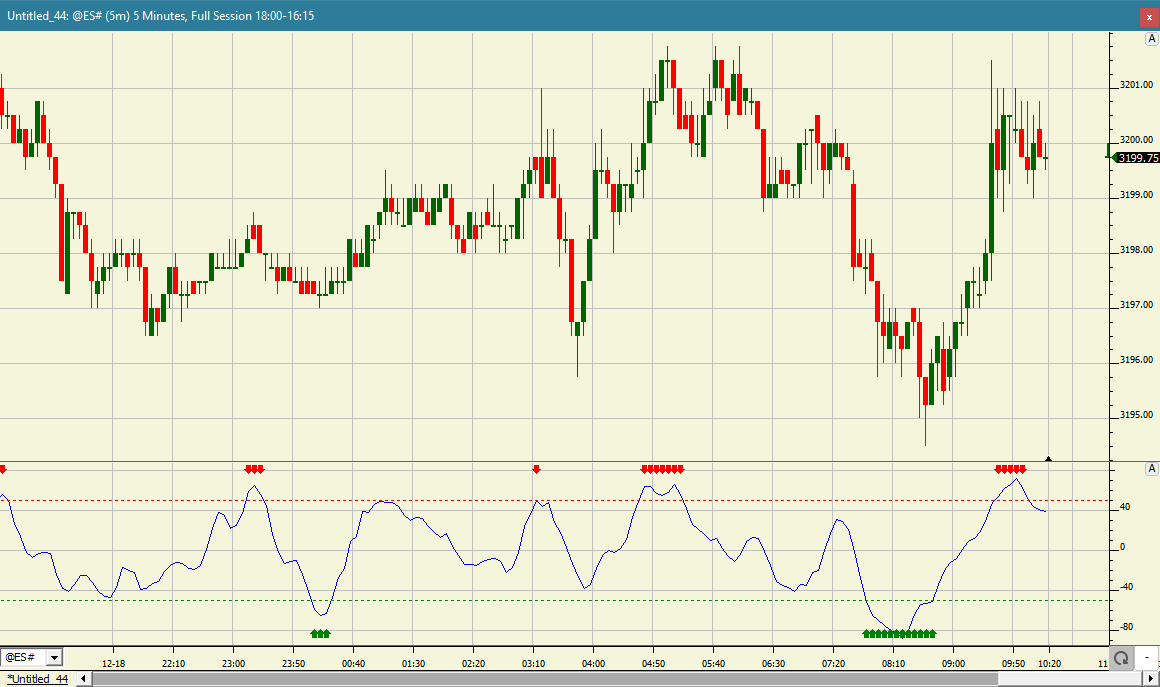
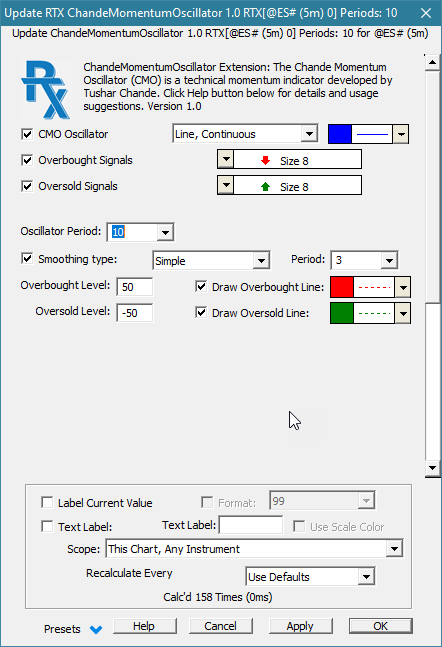
The Chande Momentum Oscillator (CMO) is a technical momentum indicator developed by Tushar Chande. The CMO indicator is created by calculating the difference between the sum of all recent higher closing bar changes and the sum of all recent lower closing bar changes. This result is then divided by the sum of all price changes over the specified number of bars. Finally, the result is multiplied by 100 to give the CMO a range -100 to +100. Typically, an instrument is considered to be overbought when the raw value of the oscillator is above 50 and oversold when it is below -50. The Investor/RT implementation enables setting the over bought and over sold levels and further enables the oscillator to be smoothed using a moving average of your choice. Smoothing is typically done with a shorter term smoothing period, e.g. 3 bars. Over bought or over sold signals would then occur only when the smoothed CMO reaches the specified extreme levels. In RT 14, the CMO RTX extension can be referenced within RTL formulas using the CMO token, e.g. the RTL expression CMO > 50 can be used in whole or as a part of a more complex formula to signal a potential sell side opportunity.
You can also look for signals based on the CMO crossing above or below a signal line composed of a 9-period moving average of a longer period CMO. In RTL this formulation (for crossing above) is: CMO.1 < CMO_MA AND CMO > CMO_MA where CMO is setup in RTL as the raw or short term smoothed CMO and CMO_MA is setup as a longer term smoothed CMO.
If underlying price make a new high or low that is not confirmed by the CMO, the divergence can signal a price reversal. For example, using a CMO period of 20 bars, the STAT token can be setup to find the highest close over 20 bars, so CL >= STAT indicates that current price is at a new high. Thus CL >= STAT AND CMO < CMO_MA would indicate a new high when the CMO remains below average, a divergence. The RTX Divergence extension may also be used to detect divergence of the CMO trend and current price trend.
Presentation